如何理解 JS 原型(隐式原型和显示原型)三座大山之一
通过一些例子来说明,首先定义
js
class People {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
eat() {
console.log(`${this.name} eat something`);
}
}
//子类
class Student extends People {
constructor(name, number) {
super(name);
this.number = number;
}
sayHi() {
console.log(`姓名${this.name},学号${this.number}`);
}
}
//实例化
const xialuo = new Student('夏洛', 100);
console.log(xialuo.name, xialuo.number); //夏洛 100
xialuo.sayHi(); //姓名夏洛,学号100
xialuo.eat(); //夏洛 eat something类型判断 - instanceof
js
console.log(xialuo instanceof Student); //true
console.log(xialuo instanceof People); //true
console.log(xialuo instanceof Object); //truejs
console.log([] instanceof Array); //true
console.log([] instanceof Object); //true
console.log({} instanceof Object); //trueclass 的原型本质是什么?实际上是函数,可见是语法糖
js
console.log(typeof People); //function
console.log(typeof Student); //function原型
js
console.log(xialuo.__proto__); //隐式原型
console.log(Student.prototype); // 显示原型
console.log(xialuo.__proto__ === Student.prototype); // true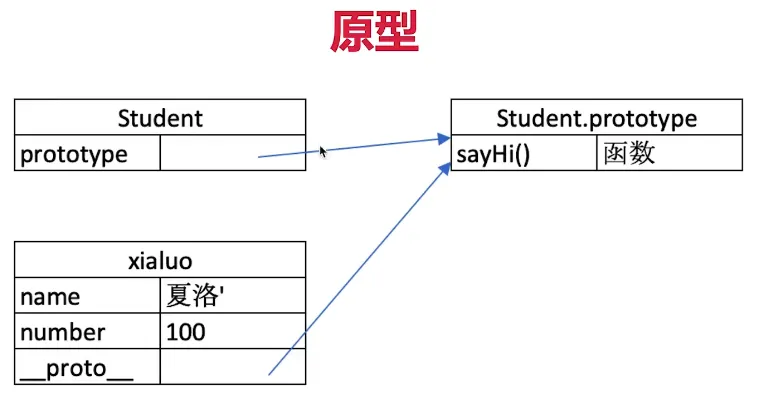
原型关系
- 每个 class 都有显示原型 prototype
- 每个实例都有隐式原型
__proto__ - 实例的
__proto__指向对应 class 的 prototype
基于原型的指向规则,获取属性或执行方法时
- 先在自身属性和方法寻找
- 如果找不到则自动去
__proto__中查找